In the subsequent half century, Finland has made a remarkable transformation from an agricultural and forest economy to a diversified modern industrial economy; per capita income is now among the highest on Western Europe.
Finland is known for its high level of technology and outstanding architecture and design. Successful businesses such Rovio, Marimekko ja Wärtsilä are recognized all over the world. Finnish conductors, contemporary composers and singers are also active in forging their reputations abroad. Finns also have a real passion for sports and their patriotic spirit is aroused in international ice hockey games, skiing competitions, athletics and motor sports.
Finland is a welfare state with the aim of securing its inhabitants equal opportunities for a good life. Education is an essential part of that. The main aim of the Finnish educational system is to ensure that the entire population has Access to education and training. The principle of lifelong learning is an important principle for all education provision, from basic schooling to adult education.
The people
Population: 5.4 million, 15,7 inhabitants per km², the inhabitants in the urban areas form 63 % of the entire population.
Average life expectancy: Men 76 years, women 83 years.
Language: The official languages are Finnish (spoken by 91 %) and Swedish (5,4 %). English is widely spoken.
Religion: 85 % Evangelical Lutheran.
Literacy: 100 %
State and government
Independency: Declared on 6 December 1917.
Form of Covernment: Parliamentary democracy with multiparty political system.
Parliament: 200 members in one chamber, elected every 4 years in a direct vote.
Head of State: President of the Republic, elected every 6 years in a direct vote Internatonal cooperation: Member of United Nations since 1995 and European Union since 1995.
Society and economy
Key features: High standard of education, social security and health care, all financed by the state.
GDP per capita: 37 819 euros (2016)
Main exports: Electrotechnical goods, metal products, machinery, transport equipment, wood and paper products, chemicals, 1/3 of GDP comes exports.
Currency: Finland was the only Nordic state to join the euro system at its initiation in January 1999.
Geography and climate
Area: 338 424 km², the sixht largest country in Europe.
Coast line: 1250 km. More than 200 000 lakesand 180 000 islands. 3/4 of the land is covered by forest, which is the most important natural resource of Finland.
Capital: Helsinki (1.25 million inhabitants inte metropolitan area)
Climate: Great contrasts – cold winters but fairly warm summers.
The Finnish educational system
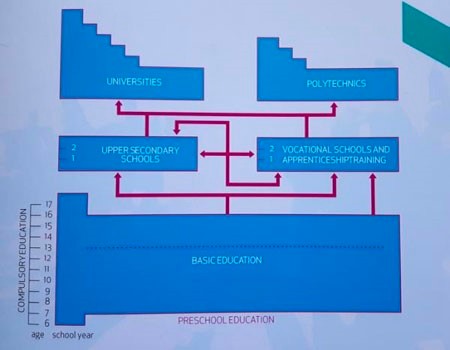
In Finland Basic education lasts nine years. After comprehensive school, upper secondary education comprises general and vocational education. The primary aim of educational system is lifelong learning. The aim is to ensute that everyone has equal learning opportunities regardless of social background. Nearly all Finnish adolescents continue their education after comprehensive school.
Vamia offers a wide range of vocational qualifications providing comprehensive vocational skills in the chosen field and in working life. The education spans three years. After the initial vocational qualification you can continue with further vocational education coprising further and specialist vocational qualifications or higher education at polytechnic or univerisyt level. A polytechnic degree requires 3.5-4.5 years of full-time study.
General upper secondary education prepares the students for the national matriculation examination. The education usually takes three years to complere and consists of a wide selection of partly optional subjects. After upper secondary school the student can apply for Basic vocational education or higher education at a polytechnic or university.
The universities focus on scientific research and education, while the polytechnics offer education on a more practical basis. At the universities you are able to take Bachelor’s and Master’s degrees, and postgraduate licentiate and doctoral degrees.
Since the education system is part of the public sector, education in Finland is free of charge. Students also receive different kinds of public aid for housing, meals and health care etc.
